Boltzmann distribution
The Boltzmann distribution is a fundamental concept in Classical Statistical Mechanics that describes the distribution of particles over various energy states in a system at thermal equilibrium.
The Boltzmann distribution shows that at thermal equilibrium, the probability of finding a particle in a particular energy state is not equal for all energy levels. Instead, it decreases exponentially with the energy of the state. This means that lower energy states are more populated than higher energy states.
The probability
where:
is the base of the natural logarithm, is the energy of the state, is the Boltzmann constant, is the absolute temperature of the system, and is a normalization factor that ensures the total probability across all states sums to 1. It is calculated as the sum over all possible energy states: .
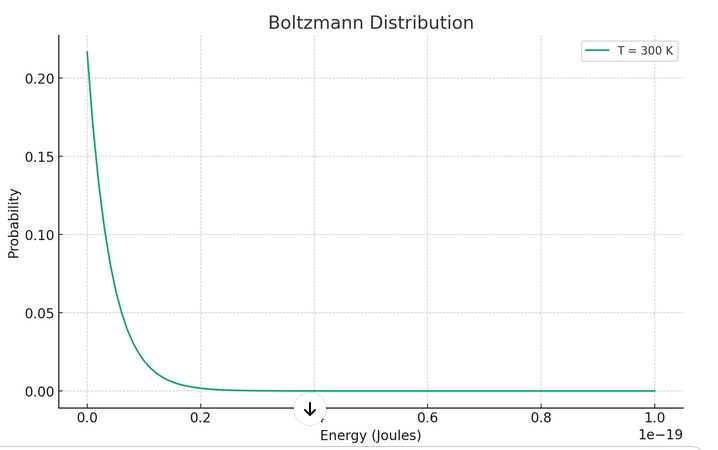
It's important to note that the Boltzmann distribution applies to systems in thermal equilibrium, where the temperature is uniform throughout the system, and the system's macroscopic properties do not change over time.