Gauge theory
See the key example Time zones example.
Gauge theory is a term that refers to a quite general type of theories in physics which share some key concepts. In this note we are going to name them, relating them with their mathematical counterpart.
In a gauge theory we start with a manifold
with typical fibre
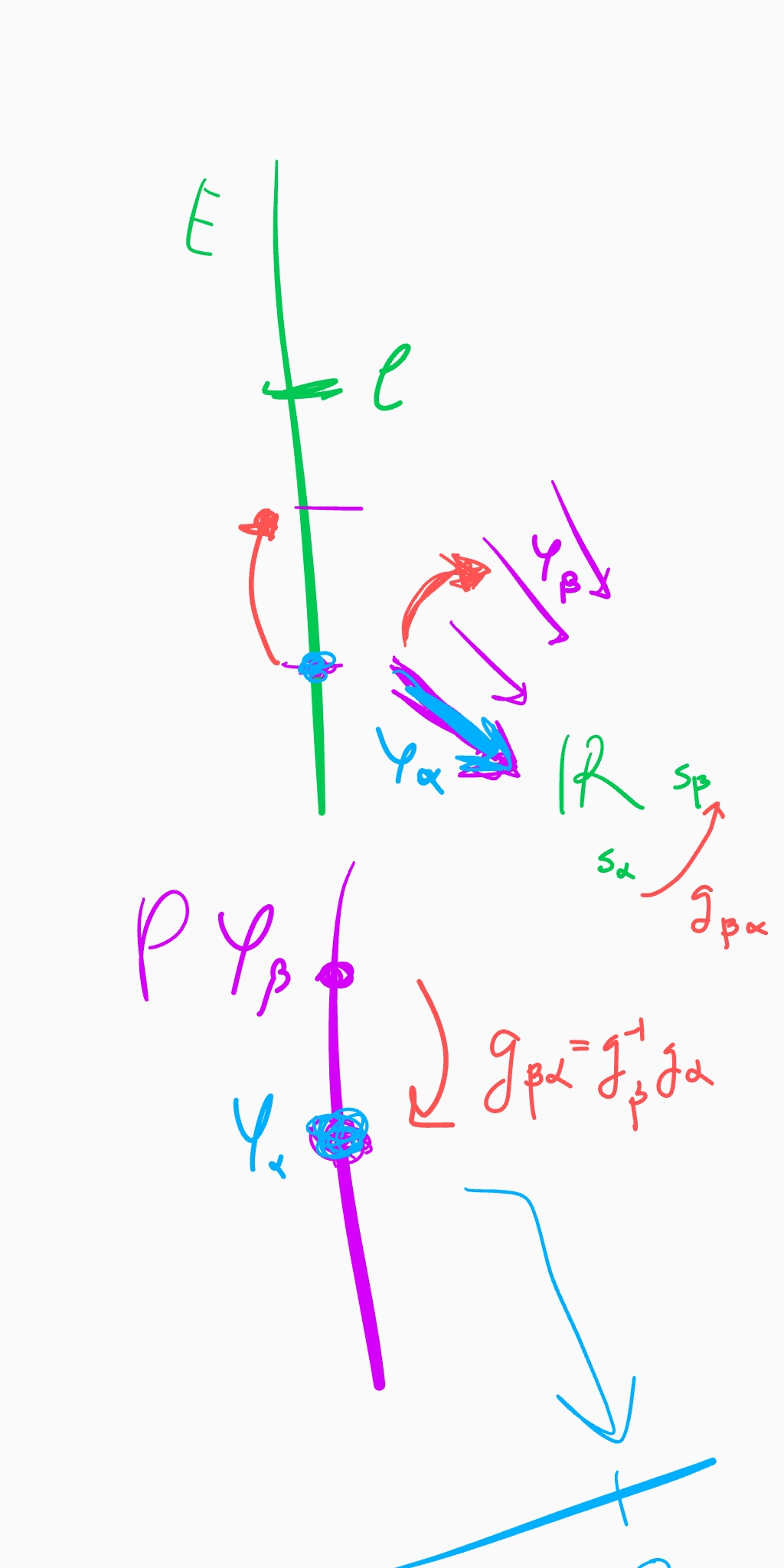
A local (global) section of the associated principal bundle
is called a local (global) gauge, and the choice of such a section is called gauge fixing. As it is said here, it let us to speak of the components of the matter field respect to this gauge fixing. In a sense, fixing a gauge is like specifying a reference frame in
Given any other gauge
such that
Observe that given a trivialization
and then, any local matter field
can be expressed by
given by the components of
See the note principal bundle for more details.
A principal connection in
We can express
Examples
- The time zone model. See me paper attempt.
- Physical gauge theories describe fermions ("particles") as complex-valued functions on a principal bundle over space-time, and bosons ("forces") as principal connection on a principal bundle (see [Sharpe 1991] page 172).
- See the meteor tracking problem at [Sharpe 1991] and [xournal 130]
Enfoque Gauge on a point