Lie derivative
It is a way to differentiate in any differential manifold. Let's consider a vector field
We can also pull back with
Personal interpretation:
Think of a "discretized" version of the flow of
In other words, suppose
See also relation of Lie derivative, covariant derivative and torsion.
Properties and Alternate Notations
It can be demonstrated that:
Or in another notation:
Here,
Moreover, it also coincides with the Lie bracket defined in Lie bracket:
In fact, there is a discussion in the mentioned reference that the annulment of the bracket implies the commutativity of flows, which is a very similar idea to the one presented above.
The Lie bracket of two vector fields,
Lie transport or Lie dragging
The Lie transport of a vector 'Y' through a field 'X' is also worthy of discussion. It would consist of applying 'd X_t( \cdot )' to the vector 'Y' to carry it to different locations. Although it may seem similar to parallel transport, there are many differences:
- Lie transport can be visualized as the transport of a river. It does not have to preserve actual parallelism, but depends on the current of that particular river, or rather, on the selected field 'X'. In fact, there need not be an underlying idea of parallelism since the manifold does not need to have a scalar product or anything to measure angles or distances.
- Continuing with the river interpretation, the Lie derivative
measures how the field 'Y' varies for an observer who is flowing in the river. See the following picture:
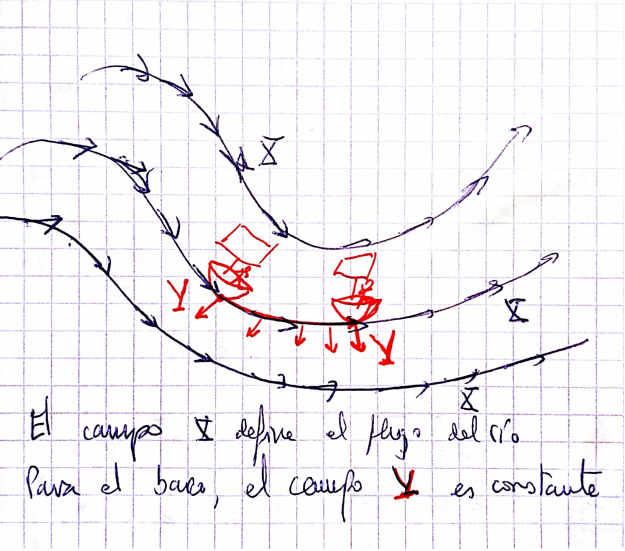
- Lie transport does not allow to transport a vector 'Y' in
to an arbitrary point , but only carries it to points of the orbit . - Lie transport not only depends on the curve connecting the points but also on the entire surrounding vector field, on the entire flow. In contrast, for parallel transport, only the selected curve connecting the points influences.
- From a more operational standpoint, the Lie derivative is a natural way to generalize the directional derivative of
to any manifold. In other words, just like the usual directional derivative verifies the Leibniz rule:
However, it lacks one property of the usual derivative: it is not tensorial. In what sense? Well, because its dependence on the vector that provides the direction of derivation, 'X', is only
as is the case with tensors. There are other ways to generalize the directional derivative that do have this property, in fact, they resemble covariant tensors. For this reason, they are called covariant derivatives and are denoted by
More about Lie derivative and connections:
See the relation of Lie derivative, covariant derivative and torsion.