Singular value decomposition
I don't know how I have not learned this until today because it is very important.
Given any real square matrix
where
The meaning of this is easy: any linear transformation of a vector space can be obtained by a rigid transformation (rotation or reflection), followed by a scale change in the main axis direction (and different scales could be applied in every axis) and finally followed by another rigid transformation.
It is related to the polar decomposition.
Visualization: see this web.
Non square matrices
This also works for non square matrices. Consider that
The
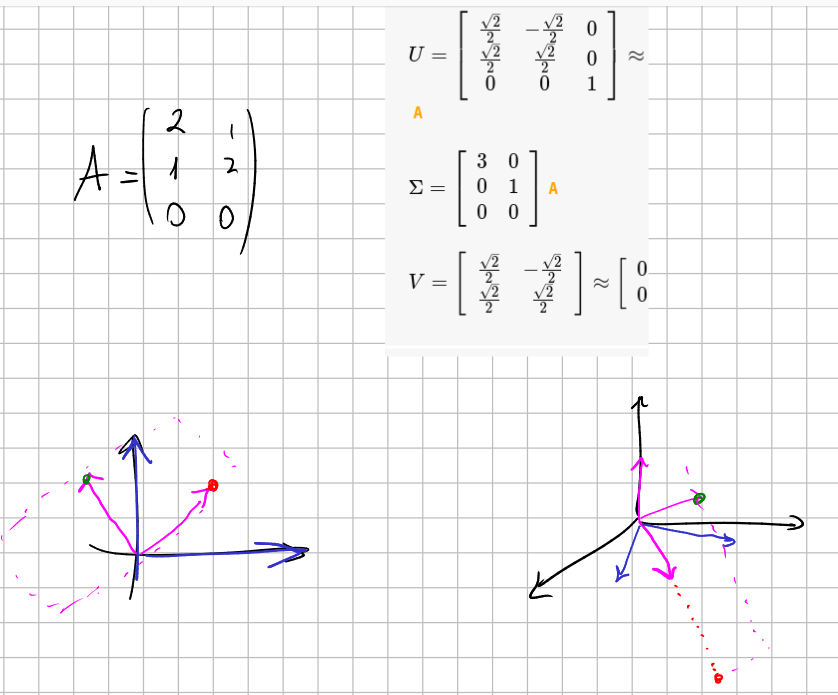
It is related to matrix diagonalization. Indeed they are equal when the matrix is symmetric positive-demidefinite.